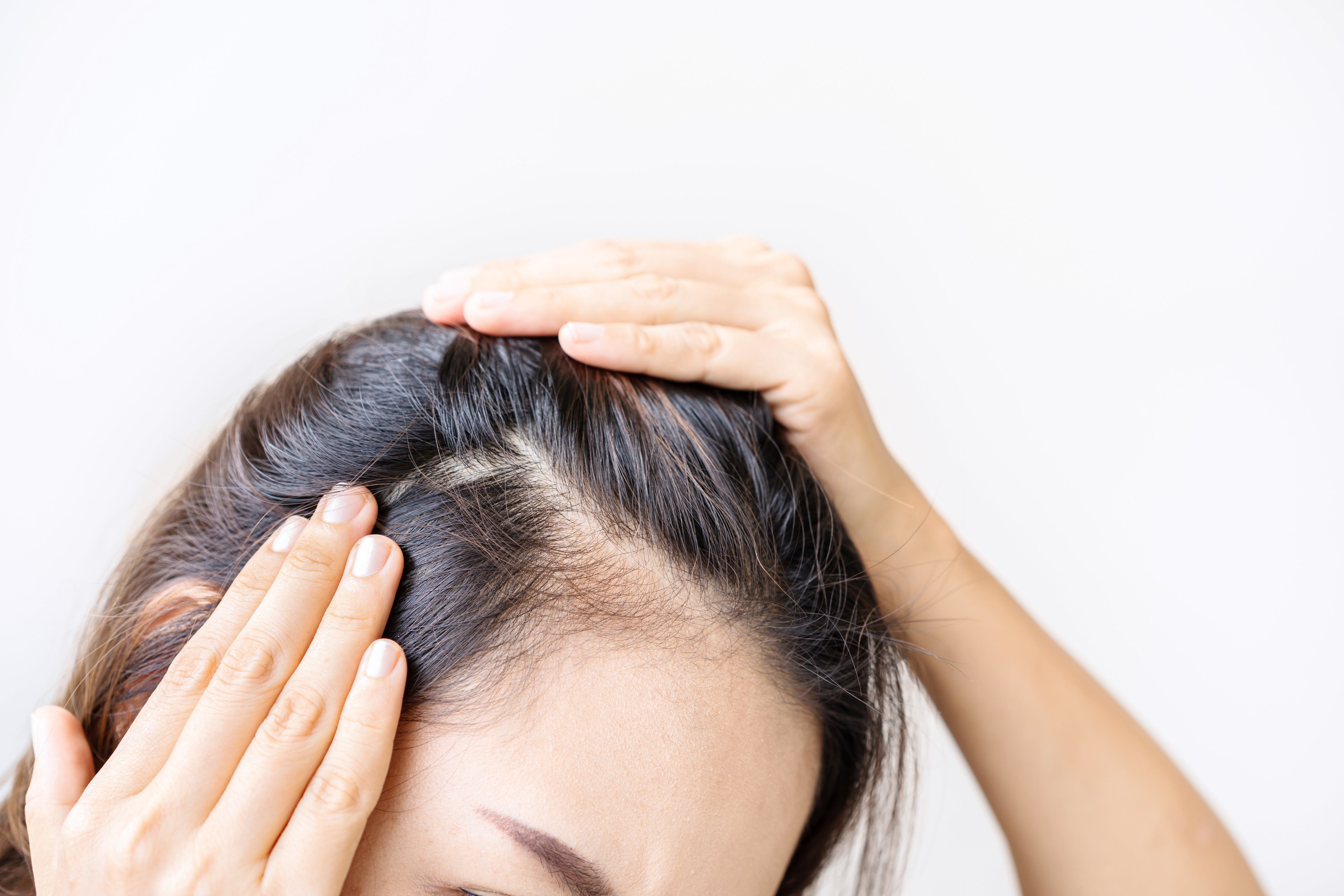

Hair Today, Gone Tomorrow? Understanding & Addressing Women’s Hair Thinning
By Dr. Tahani Williams, M.D.
Hair thinning in women is more common than many realize. While hair loss is often associated with men, millions of women experience thinning hair, excessive shedding, or bald spots — and the emotional impact can be significant. If you’ve noticed more hair in your brush, on your pillow, or in the shower drain, you’re not alone. The good news: help is available.
Why Hair Thinning Happens in Women
Hair thinning in women is harder to recognize and diagnose than male pattern baldness. It can appear as overall volume loss, a widening part, or more visible scalp. The causes are often multifactorial:
1. Hormonal Changes
Fluctuations during menopause, pregnancy, or after stopping birth control can disrupt the hair growth cycle. Estrogen normally prolongs hair’s growing phase, so when levels decline, hair thinning increases.
- Postpartum hair loss peaks 3–4 months after giving birth.
- Menopause often leads to permanent changes in hair texture and volume.
2. Genetics
Female Pattern Hair Loss (FPHL), the most common cause of hair thinning in women, is largely hereditary. It typically starts at the part line and gradually spreads. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, FPHL rarely leads to complete baldness but can cause significant thinning.
3. Stress and Trauma
Stress-related hair loss, known as telogen effluvium, can be triggered by:
- Major life changes (divorce, grief, job loss)
- Illness or surgery
- Crash dieting or nutritional deficiencies
Fortunately, this type of hair loss is often temporary once the underlying cause is addressed.
4. Medical Conditions
Underlying health issues that contribute to hair loss include:
- Thyroid disorders
- PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome)
- Autoimmune conditions such as alopecia areata
- Iron-deficiency anemia
Resources like the Mayo Clinic emphasize the importance of diagnosis before treatment.
5. Styling Habits & Hair Products
Frequent heat styling, chemical treatments, tight hairstyles, or harsh shampoos can cause scalp irritation and traction alopecia. Over time, these practices damage hair follicles and worsen thinning.
Common Types of Hair Loss in Women
|
Type |
Description |
Reversible? |
|---|---|---|
|
Telogen Effluvium |
Sudden shedding due to stress/illness |
Yes |
|
Female Pattern Hair Loss |
Gradual thinning at part/crown |
Often progressive |
|
Alopecia Areata |
Autoimmune-related patchy hair loss |
Sometimes |
|
Traction Alopecia |
Caused by tight hairstyles/damage |
Yes, if caught early |
|
Scarring Alopecia |
From scalp inflammation/injury |
Often permanent |
Signs You May Be Experiencing Hair Loss
- Ponytail or bun feels thinner
- Widening part line
- Excess hair on pillow or brush
- Scalp becoming more visible in bright light
- Patchy bald spots
If these signs persist for several months, consult a dermatologist.
Treatment Options for Women’s Thinning Hair
1. Topical Treatments
-
Minoxidil (Rogaine) is FDA-approved for women and can stimulate regrowth.
2. Supplements
- Nutrients like biotin, vitamin D, iron, zinc, and omega-3s support hair health.
- Too much biotin may interfere with lab tests — always consult your doctor first.
3. Healthy Hair Habits
- Use gentle, fragrance-free shampoos and conditioners
- Limit heat styling and harsh chemical treatments
- Avoid tight hairstyles overnight
4. Medical Interventions
- Treat underlying conditions (thyroid, PCOS, iron deficiency)
- Manage stress with mindfulness or therapy
The Emotional Side of Hair Loss
Hair isn’t just cosmetic — it’s linked to identity and confidence. Thinning hair can lead to stress, anxiety, and self-consciousness. Seeking support, whether through a dermatologist, therapy, or community groups, is an important part of care.
How Cleure Supports Hair & Scalp Health
At Cleure, we believe sensitive scalps deserve gentle care. Our dermatologist-recommended, National Eczema Association–approved formulas are fragrance-free, sulfate-free, non-comedogenic, and pH-balanced — ideal for women experiencing hair thinning and scalp irritation.
-
Sensitive Skin Shampoo – gentle cleansing without stripping natural oils
-
Fragrance-Free Conditioner – restores softness without irritation
-
Shampoo & Conditioner Duo – designed for long-term scalp balance
-
Full Hair Care Collection – complete support for sensitive scalps
Tip: Pair your shampoo with a fragrance-free body wash to reduce scalp and skin triggers.
FAQs About Thinning Hair in Women
What causes thinning hair in women?
Common causes include hormonal changes, genetics, stress, nutritional deficiencies, medical conditions, and harsh styling habits.
What are the “big 3” for thinning hair?
The most widely discussed are minoxidil, finasteride, and low-level laser therapy. For women, only minoxidil is FDA-approved.
How do women fix thinning hair?
Address the root cause, adopt scalp-friendly habits, use gentle hair products, and consult a dermatologist for treatments like minoxidil or PRP.
Can women’s hair grow back after it has started thinning?
Yes, depending on the cause. Conditions like telogen effluvium or traction alopecia are often reversible, while genetic FPHL can be managed but not fully reversed.
Does biotin really thicken hair?
Biotin supports hair strength, but evidence is mixed on its ability to regrow hair. It is most helpful if you are biotin-deficient.
Start Your Hair Care Journey
Thinning hair in women is common — and treatable. Whether the cause is genetics, hormones, stress, or scalp sensitivity, the right combination of medical support and gentle hair care can make a difference.
Explore Cleure’s Hair Care Collection for dermatologist-recommended products that calm sensitive scalps and support healthier hair.
References:
1. American Academy of Dermatology Association, December 2022.
2. Mayo Clinic, January 2024.


Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.